Japan

高等教育資格承認情報センター
The National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan (NIC-Japan)
National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education (NIAD-QE)
1-29-1 Gakuen-nishimachi,
Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan
Phone Number: (+37410) 53 09 04 – (+37491) 429 835
Fax: (+37410) 53 09 04
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: https://www.nicjp.niad.ac.jp/en
Education
The education system of Japan starts with pre-school education, followed by six years of elementary education, and six years of secondary education (comprised of three years of lower secondary and three years of upper secondary education), which leads to a wide range of higher education. The nine years of elementary and lower secondary education cover compulsory education.
The principles of education in Japan are established by the Basic Act on Education (教育基本法). The basis of the school education system is defined by the School Education Act (学校教育法).
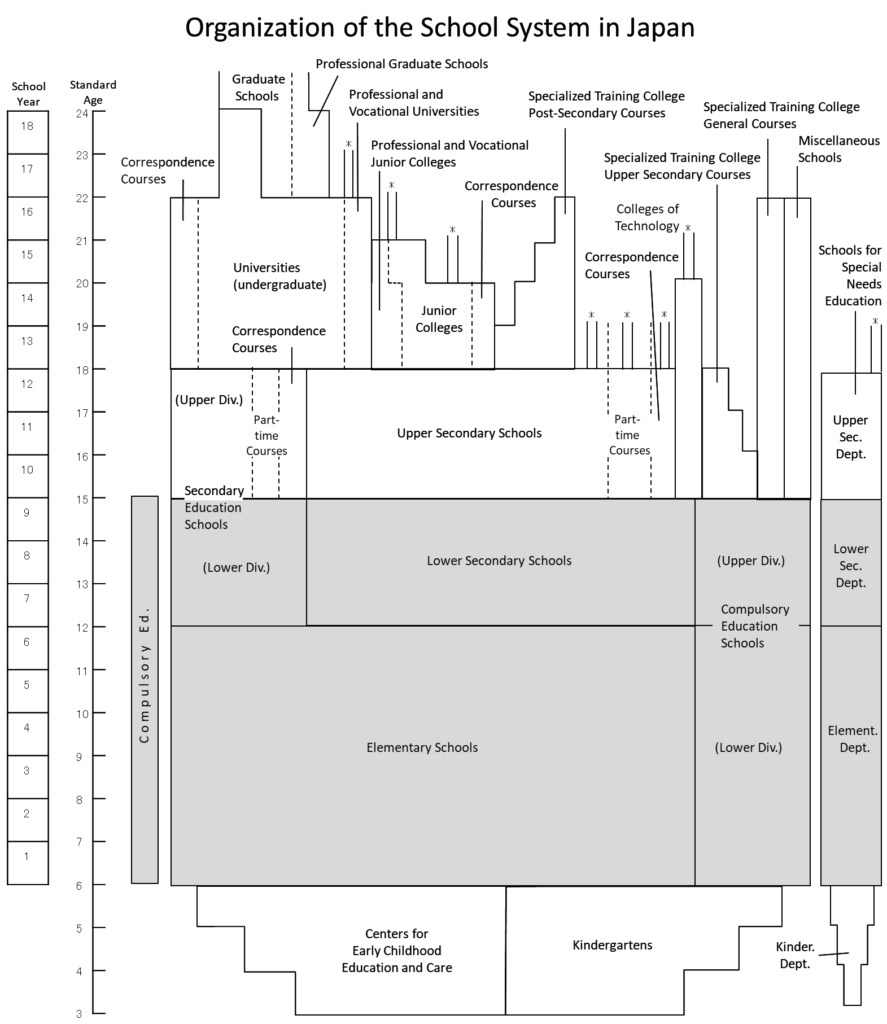
Notes:
(1) This diagram shows schools regulated by the School Education Act.
(2) The scope of ‘higher education institutions’ subject to the UNESCO ‘Asia-Pacific Regional Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications in Higher Education’ includes some educational institutions operated by government ministries and agencies (National College of Nursing, Japan; Polytechnic University; and National Fisheries University), in addition to the above.
(3)*indicates advanced courses
(4) Upper secondary schools, upper division of Secondary Education Schools, universities, junior colleges, and upper secondary department of Schools for Special Needs Education can have separate courses with course terms of 1 year or more.
(5) A child aged from 0 to 2 years old can attend Centers for Early Childhood Education and Care because it functions as school as well as child welfare institution.
(6) Age and admission requirements for Specialized Training College General Courses and Miscellaneous Schools are not defined uniformly.
Pre-school education includes kindergartens (幼稚園 yochien), day care centres (保育所 hoikusho), and “centres for early childhood education and care” (認定こども園 nintei-kodomo-en).
In relation to elementary and secondary education, typical institutions include elementary schools (小学校 shogakko) for elementary education and lower secondary schools (中学校 chugakko) and upper secondary schools (高等学校 kotogakko) for secondary education.
There are also schools for special needs education (特別支援学校 tokubetsu-shien-gakko) (departments of kindergarten, elementary, lower secondary, and upper secondary) for children and students with disabilities.
In addition, in 1998, it became possible to establish six-year Secondary Education Schools (中等教育学校 chuto-kyoiku-gakko) which combine lower and upper secondary education, and in 2016, it became possible to establish Compulsory Education Schools (義務教育学校 gimu-kyoiku-gakko) which combine elementary and lower secondary education.
For the upper division of Secondary Education Schools and upper secondary schools, there are also schools that offer part-time courses (定時制 teiji-sei) in the evening or at other specific times, correspondence courses (通信制 tsushin-sei) that offer distance education, and 高等専修学校 koto-senshu-gakko which is Upper Secondary Courses of Specialized Training Colleges (専修学校高等課程 senshu-gakko-koto-katei).
More information is available at the National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan(NIC Japan) website.
There is no legal definition on the scope of HEIs in Japan.
The scope of higher education institutions (HEIs), subject to the Asia-Pacific Regional Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications in Higher Education (known as the Tokyo Convention) is defined by the “Guideline on Recognition of Higher Education Qualification – Asia-Pacific Regional Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications in Higher Education” (Japanese language only).
According to the Guideline, HEIs include universities (大学), graduate schools (大学院), junior colleges (短期大学), Colleges of Technology (KOSEN) (高等専門学校) , and Professional Training Colleges (専門学校) (except for Prefectural Colleges of Agriculture), and three educational institutions operated by government ministries and agencies (省庁大学校). Based on the type of establishing body, HEIs are categorized as national (国立), public (公立), or private (私立).
Under the category of “university”, there are undergraduate programmes, junior colleges, and graduate schools. Within them, universities and junior colleges that aim to educate professionals through a high-quality vocational education are Professional and Vocational Universities (PVU, 専門職大学) and Professional and Vocational Junior Colleges (PVJC, 専門職短期大学), and graduate schools that specialize in fostering highly-specialized professionals with flexible and practical education, known as Professional Graduate Schools (専門職大学院).
According to the School Basic Survey, as of May 1, 2019, there were 786 universities (including undergraduate and graduate schools), 326 Junior Colleges, 57 Colleges of Technology, 2,805 Professional Training Colleges, and 3 educational institutions operated by government ministries and agencies in Japan.
Information is available at the website of the National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan (NIC-Japan)
The list of higher education qualifications, their awarding institution types, and further accessible education levels are shown below.
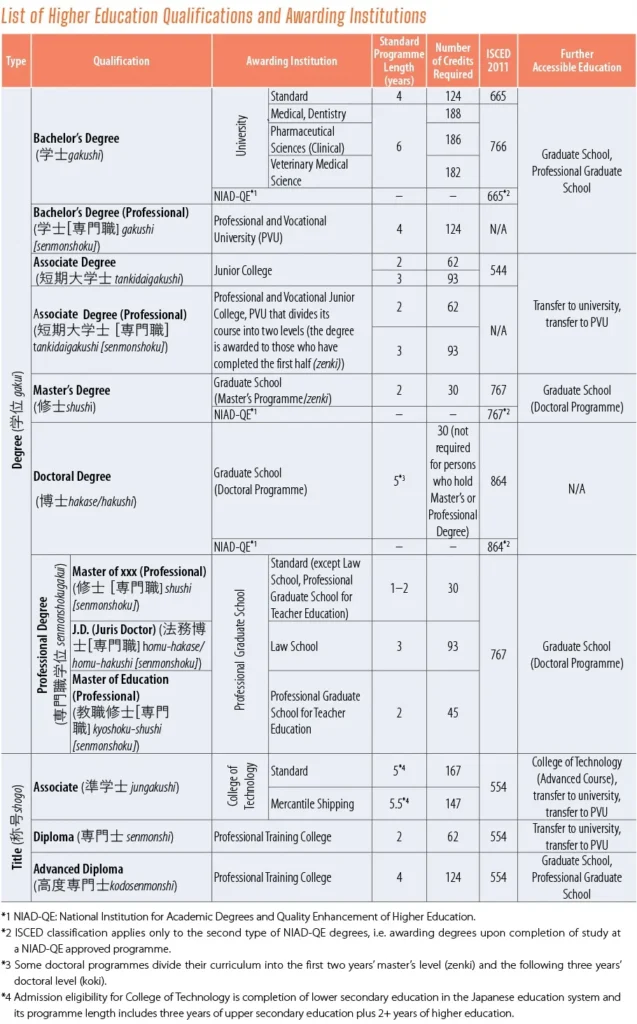
NIAD-QE awards degrees in two schemes: (1) for graduates of Junior Colleges and Colleges of Technology, who have accumulated credit hours to a certain level of learning (such as a bachelor’s degree); and (2) for those who have completed courses at educational institutions operated by government ministries and agencies recognized as equivalent to university undergraduate programmes or graduate programmes (bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees).
In addition to higher education institutions explained in the Higher Education section, the National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education (NIAD-QE) can award bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees based on the Degree Regulations (Ordinance of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture No.9 of 1953).
NIAD-QE evaluates various learning outcomes achieved at the higher education level and awards degrees to persons recognized as having academic ability equivalent to, or greater than, those who have graduated from a university undergraduate programme or who have completed graduate school.
Please refer to the NIC-Japan and NIAD-QE website for more details on qualifications and on Scheme 1, and Scheme 2.
National Information Centre (NIC) Information and Activities
Japanese government acceded the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Regional Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications in Higher Education (known as the Tokyo Convention) in December 2017, and accepted the Global Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education (known as the Global Convention) in September 2022. Both conventions aim to promote international mobility of students and academics between State Parties, by having each Party prepare systems to facilitate assessment and recognition of higher education qualifications for applicants seeking for further education or employment in another Party.
The parties to the Tokyo Convention and the Global Convention are required to establish and maintain a national information center (NIC) or similar entities mainly for disseminating information about their own country’s higher education system, so that other Parties can smoothly evaluate and recognize its higher education qualifications.
National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan (NIC-Japan) was established within the National Institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education (NIAD-QE) on September 1, 2019 as Japan’s official NIC. It works to disseminate information both domestically and internationally about Japanese higher education system and qualifications, a list of Japanese higher education institutions, links to relevant websites on education systems and qualifications of other countries. The center also networks with NICs in other Parties and conducts relevant surveys and research.
News /Events
The National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan (NIC-Japan) publishes news here.
Projects
The National Information Center for Academic Recognition Japan (NIC-Japan) carries out the following tasks:
- Provides information on the higher education system of Japan
- Provides information on education systems in other countries, especially State Parties of the Tokyo Convention
- Builds a global network for recognition of higher education qualifications
- Conducts relevant surveys and research
- Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- The Japan Association of National Universities (JANU)
- Japanese College and University Portraits (JPCUP)
- National Institute of Technology, Japan
- National Association of Vocational Schools of Japan
- Japan Student Services Organization(JASSO)
- Japan Network of Certified Evaluation and Accreditation Agencies (JNCEAA)
Higher Education Institutions (HEI) Landscape and Mobility
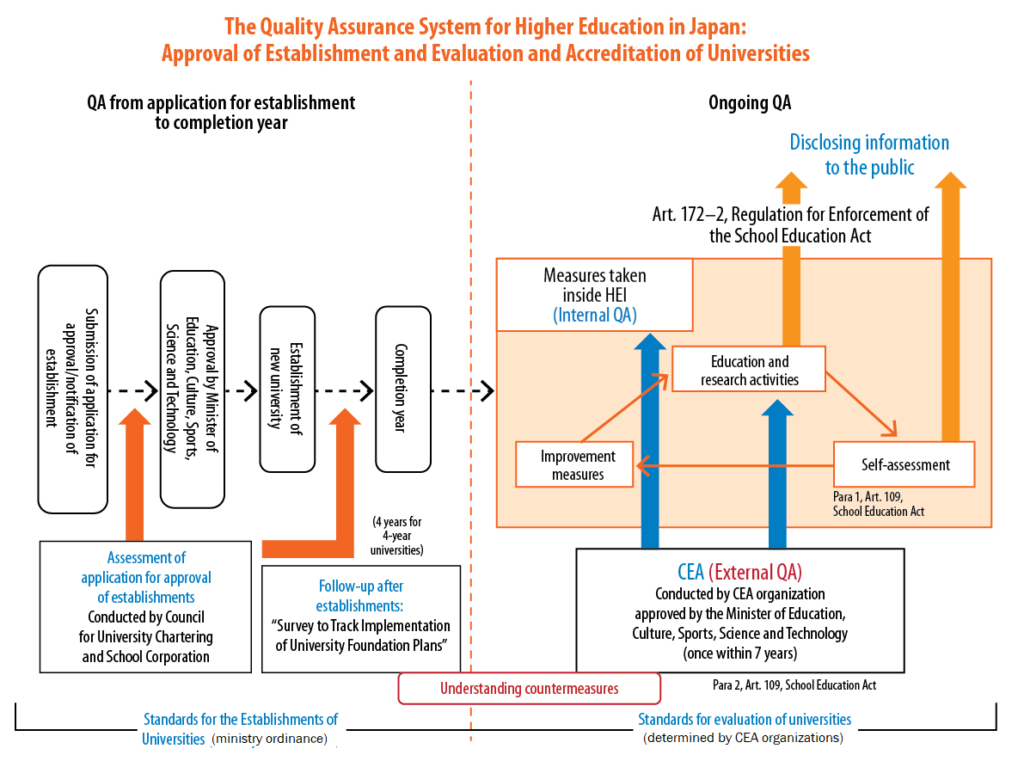
In accordance with the School Education Act, the following two systems comprise the quality assurance approach for higher education in Japan:
- Approval/notification system for establishment of universities and colleges (Article 4)
- Certified evaluation and accreditation (CEA) system (Article 109, paragraphs (2) and (3)).
Each higher education institution conducts autonomous and independent quality assurance (internal quality assurance) on education and research activities. In addition, there are public quality assurance systems in place which function together with standards for establishment and other laws and regulations, such as the Approval System of the Establishment and Certified Evaluation and Accreditation (CEA).
In principle, approval of the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is required for the establishment of a university, college, or a faculty or department in an existing university and college. Standards for the establishment of higher education institutions, including the Standards for the Establishment of Universities and Standards for the Establishment of Graduate Schools, are all based on ministerial ordinance introduced by the ministry, and exist as standards for the approval process.
The CEA system is a mandatory evaluation system in which CEA organizations conduct evaluation of the status of education and research of universities, Junior Colleges, Professional and Vocational Universities, Professional and Vocational Junior Colleges, Colleges of Technology, and Professional Graduate Schools, based on standards for evaluation and accreditation made by each CEA organization. CEA is carried out periodically as stipulated in law. Institutional CEA is conducted once within seven years for universities, Junior Colleges, etc. CEA by academic discipline is conducted once within five years for Professional Graduate Schools, etc.
Universities and colleges are required not only to undergo CEA, but also to conduct self-assessment of the conditions of educational and research activities and to disclose the results.
More details including the list of CEA organizations and quality assurance of other types of HEIs are available here.
The Japan Network of Certified Evaluation and Accreditation Agencies (JNCEAA) publishes results of evaluation and accreditation conducted by all CEA organizations that join the network.
The major initiatives of the Government of Japan for the internationalization of higher education include:
Top Global University Project (スーパーグローバル大学創成支援事業)
The Top Global University Project is a funding project that aims to enhance the international competitiveness of higher education in Japan. It provides support for world-class and innovative universities that lead the internationalization of Japanese universities. A total of 37 programmes have been selected for this project and 550,000 students and 80,000 academics have participated in programmes. This is equivalent to 20% of all universities in Japan.
Inter-University Exchange Project (Re-Inventing Japan Project) (大学の世界展開力強化事業)
The Re-Inventing Japan Project is a funding project that aims to foster human resources capable of being globally active, and to assure the quality of mechanisms for the mutual recognition of credits and grade management through an international framework. It does this by giving financial support to efforts for the formation of collaborative programmes with foreign universities that conduct study abroad programmes for Japanese students, and undertakes the strategic acceptance of foreign students. The target area of this project covers Asia, the USA, the EU, Russia, India, and Africa. About 50 programmes have been selected since the start of 2011, with a total of over 15,000 outbound students dispatched and 13,000 inbound students accepted.
Scholarships for inbound and outbound students
The Japanese Government (MEXT) Scholarship Programme (国費外国人留学生制度), covers scholarships for privately funded students, while programmes for student exchange provide financial support for international students studying in Japan.
To support outbound mobility students, there are scholarships for degree-seeking students and scholarships for short-term exchange students.
The TOBITATE! Young Ambassador Programme is a new scholarship programme for studying abroad created in cooperation among MEXT, JASSO, and the private sector.

