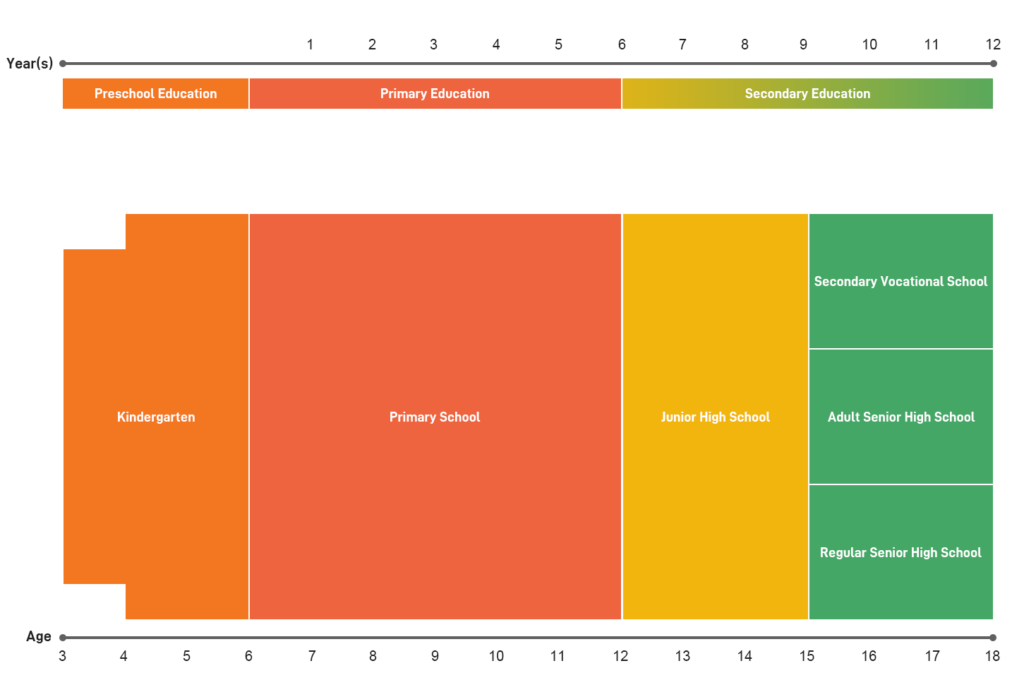
Sources: Overview of Educational Achievements in China in 2019, Number of Higher Education Institutions
Provider: Department of Development Planning, MOE
Diagram Production: CHESICC
Home | National Information Centres | China – Basic Education System

Sources: Overview of Educational Achievements in China in 2019, Number of Higher Education Institutions
Provider: Department of Development Planning, MOE
Diagram Production: CHESICC
UNESCO Regional Office in Bangkok
Mom Luang Pin Malakul Centenary Building
920 Sukhumvit Road, Prakanong,
Klongtoei, Bangkok 10110, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 UNESCO. All rights reserved.